There are two ways in which you can merge files (data sets) in SPSS. Firstly, you can merge files that contain the same variables (fields or columns) but different records or cases (rows). Secondly, you can merge files that contain the same records or cases (rows) but different variables (fields or columns).
The steps for merging files that contain the same variables but different records or cases follow below. The steps for merging files that contain the same records or cases but different variables are on the second page of this tutorial.
Merging Files: Same Variables, Different Records or Cases
The steps for merging files that contain the same variables, but different records or cases are below.
Quick Steps
- Ensure that the first file you want to merge is open in SPSS.
- Click Data -> Merge Files -> Add Cases
- Select the second file for the merge if it is open in SPSS OR
Click Browse and browse to the second file for your merge. Double-click on it. - Select Continue
- If desired, pair unpaired variables for the merged data set by holding down the CTRL key, selecting the two variables, and clicking the Pair button
- Click OK
- Click File -> Save As to save your merged file.
The Files (Data Sets)
We start from the assumption that you have imported your files into SPSS (from Excel or MySQL , for example), and that you have your first file open. This first file is known as the active data set in SPSS.
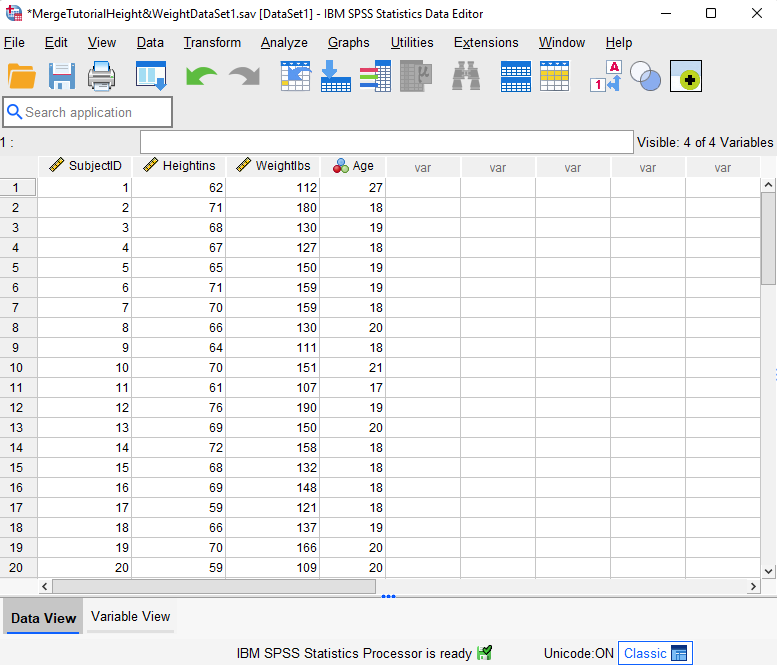
The active data set in our example contains fictitious height, weight, and age data for 40 students. We want to merge it with a second file containing the same information for another 40 students.
Merging Your Files
To merge the two files select Data -> Merge Files -> Add Cases as illustrated below:
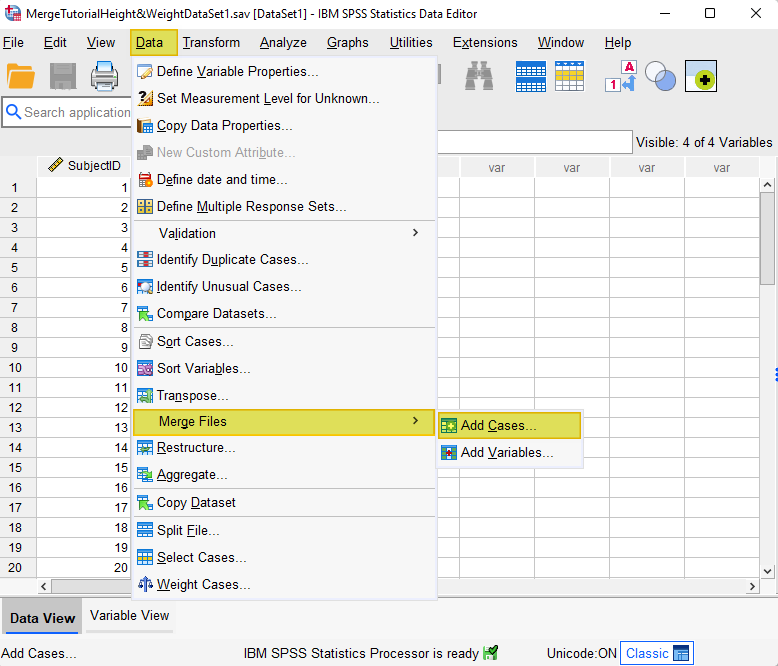
This brings up an “Add Cases to” dialog box.
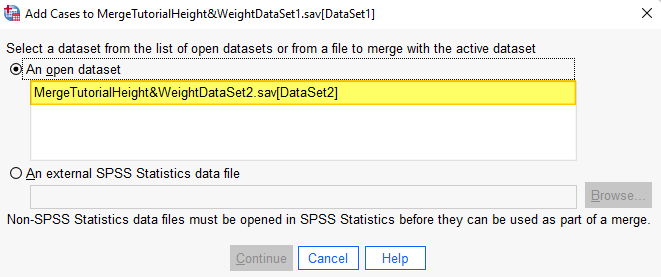
If the second file for your merge is open in SPSS, it will appear below “An open dataset” as illustrated below. Select this file.
If the second file for your merge is not open in SPSS (as is the case in the screenshot below), select Browse.
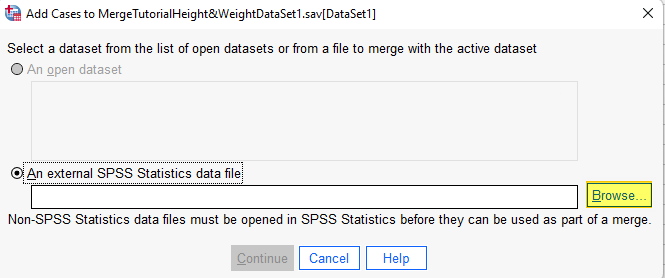
This brings up File Explorer on your computer. Browse to the file that you want to merge with the active file and double-click on it. The file pathway will then appear in the box under “An external SPSS Statistics data file.”
Select Continue.
This brings up the following dialog box. Note that, if you browsed to your second data set, DataSet2 (outlined in red below) will be replaced with your file path.
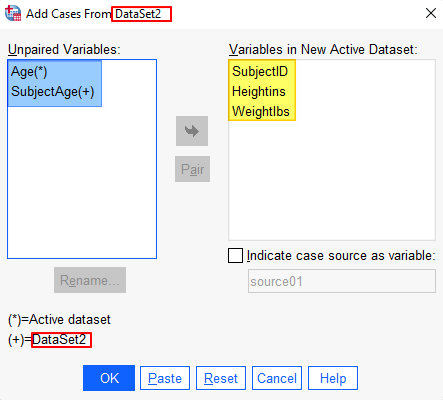
The variables that are present in both merge files will be listed in the “Variables in New Active Dataset” window (highlighted yellow above).
Creating Pairs from Unpaired Variables
If there are any variables that are present in one of your merge files but not in the other, these will appear in the “Unpaired Variables” box (highlighted blue in the screenshot above). Unpaired variables that are present in the active data set only are followed by “(*).” Unpaired variables that are present in the second data set only are followed by “(+).”
If your have variables that are present in both files but have different names in the two files, you can pair them in your merged data set. In our example, the variables “Age” in the active data set and “SubjectAge” in the second data set both contain subjects’ age, so we want to pair them. To do this, hold down the CTRL key and select your two variables in the “Unpaired Variables” box. This activates the “Pair” button. Select the Pair button to pair the two variables and move them to the “Variables in New Active Dataset” box. After we take this step, the dialog box appears as below. SPSS will use the variable name from the active data set in the merged file.
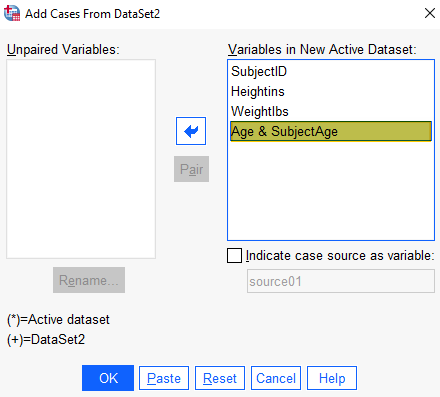
Select OK.
The Merged File
Your active data set will now contain the records or cases that you added from your second data set.
If you want to keep your first file unchanged, you should save your merged file with a new name using File -> Save As.
***************
That’s it for the first part of this tutorial. You should now be able to merge files that contain the same variables but different records or cases in SPSS. In the second part of this tutorial, we show you how to merge files that contain the same records or cases but different variables.
***************
Merging Files: Same Records or Cases, Different Variables
The steps for merging files that contain the same records or cases, but different variables are below.
Quick Steps
- Ensure that the first file you want to merge is open in SPSS
- Click Data -> Merge Files -> Add Variables
- Select the second file for the merge if it is open in SPSS OR
Click Browse and browse to the second file for your merge. Double-click on it. - Select Continue
- Ensure that One-to-one merge based on key values is selected.
- Ensure that the box for Sort files by key values before merging is checked.
- Click OK
- Click File -> Save As to save your merged file.
The Files (Data Sets)
As before, we start from the assumption that you have imported your files into SPSS (from Excel or MySQL, for example), and that you have your first file open. This first file is known as the active data set in SPSS.
Both data sets should contain an ID column to enable SPSS to match the records or cases (rows) in the merged file.
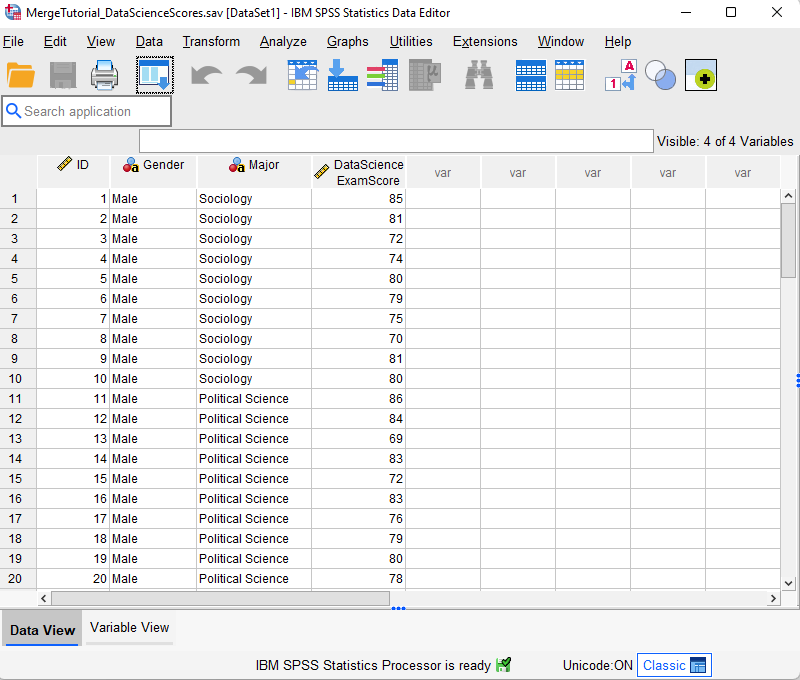
Our active data set contains the gender, major and Data Science exam scores for 60 fictitious students. We want to merge it with a second fictitious data set containing the gender, major and Research Methods exam score for the same students.
Merging Your Files
To merge the two files, select Data -> Merge Files -> Add Variables as illustrated below:
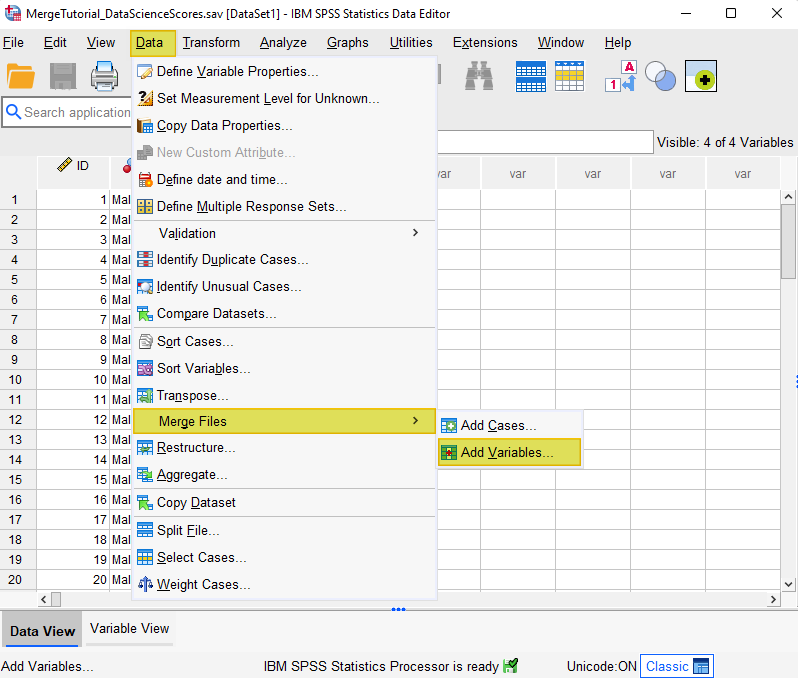
This brings up the “Add Variables to” dialog box as illustrated below.
If the second merge file is open in SPSS, it will appear in the box under “An open dataset” as illustrated below. Select this file.
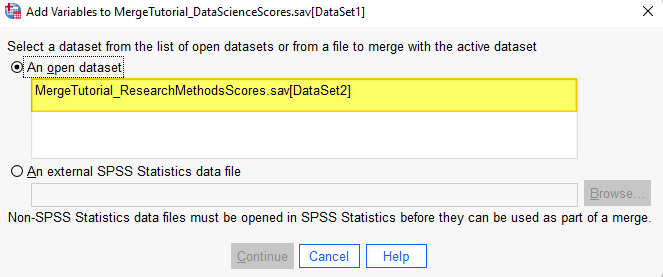
If – as in the screenshot below – the second file for your merge is not open in SPSS, select Browse.
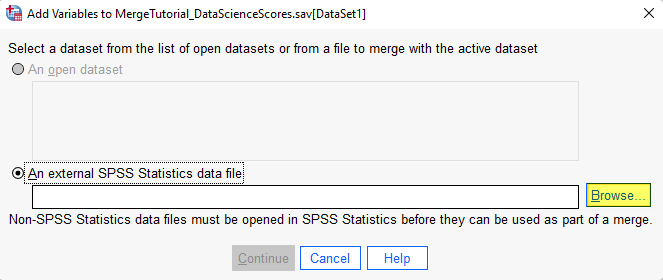
This brings up File Explorer on your computer. Browse to the file that you want to merge with the active file in SPSS and double-click on it. The file pathway will then appear in the box under “An external SPSS Statistics data file.”
Select Continue. This brings up the dialog box below.
Note that, if you browsed to your second data set, DataSet2 (outlined in red below) will be replaced with your file path.
The variables that are present in both merge files will be listed as “Key Variables” at the bottom of the dialog box. In our example, these variables are ID, gender, and major.
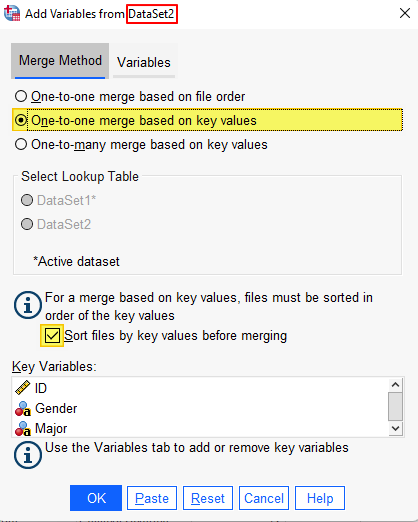
Ensure that One-to-one merge based on key values is selected. You should also ensure that the box for Sort files by key values before merging is checked.
Select OK.
The Merged File
Your active data set will now contain the additional variable(s) from your second data set. In our example, the Research Methods exam score has been added as outlined in red below.
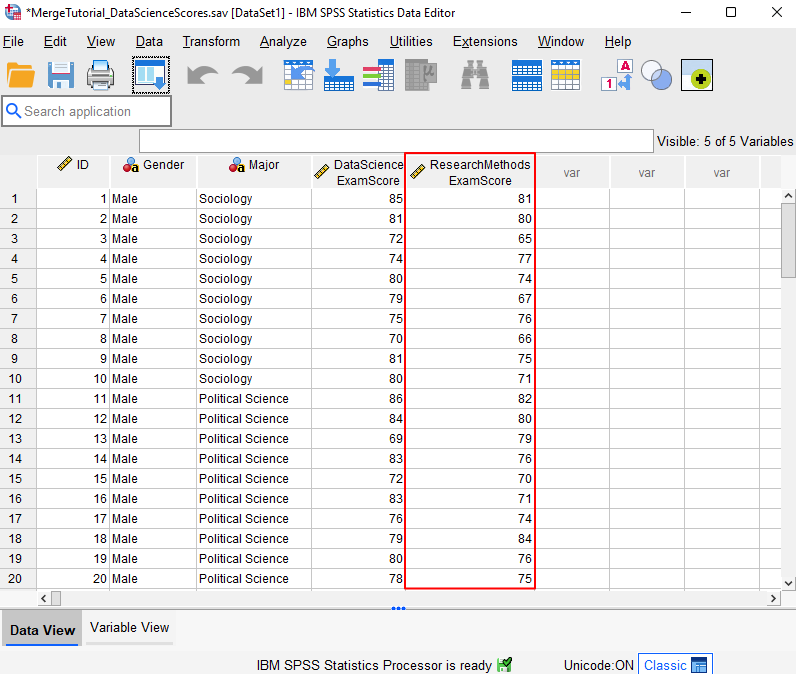
If you want to keep your first merge file unchanged, you should save your new file with a new name using File -> Save As.
***************
That’s it for the second part of this tutorial. You should now be able to merge files that contain the same records or cases but different variables in SPSS. Please see the first page of our tutorial if you want to merge files that contain the same variables but different records or cases.